Learn how to revert to a previous 5+ commits on GitHub with this simple guide for developers. Step-by-step instructions to undo changes and restore your project effortlessly.
github revert to previous commit: “a simple guide for developers”
In the world of software development, working with version control systems like Git is essential for tracking changes, collaborating with teams, and managing code effectively. GitHub, being one of the most popular platforms for hosting Git repositories, provides a suite of powerful tools that streamline the development workflow. Among these tools, the ability to revert to a previous commit is one of the most essential features, enabling developers to undo changes, correct mistakes, or experiment safely.
In this article, we will dive deep into how to revert to a previous commit on GitHub, explore why this is useful, and provide step-by-step instructions on how to do it, including the key considerations and best practices. Let’s explore the ins and outs of reverting to a previous commit in GitHub.
What Does “Reverting to a Previous Commit” Mean?
When working with Git and GitHub, every change you make to your code is saved as a commit. A commit is essentially a snapshot of your code at a particular point in time. Reverting to a previous commit means you’re undoing recent changes and restoring the state of the repository to how it was at an earlier commit.
This action is useful in many scenarios, such as:
- Accidentally committed the wrong changes: If you’ve made a mistake and committed incorrect code, reverting helps undo those changes.
- Bug introduction: Sometimes a commit introduces bugs or breaks existing functionality. Reverting allows you to return to a stable version of the code.
- Experimentation: Developers often use branches to experiment with new features. If the experiment doesn’t work out, reverting to a previous commit restores the project to its last stable state.
It’s important to note that while reverting undoes changes, it does not erase them completely. Reverts create new commits that roll back the changes, ensuring your project’s history is intact.
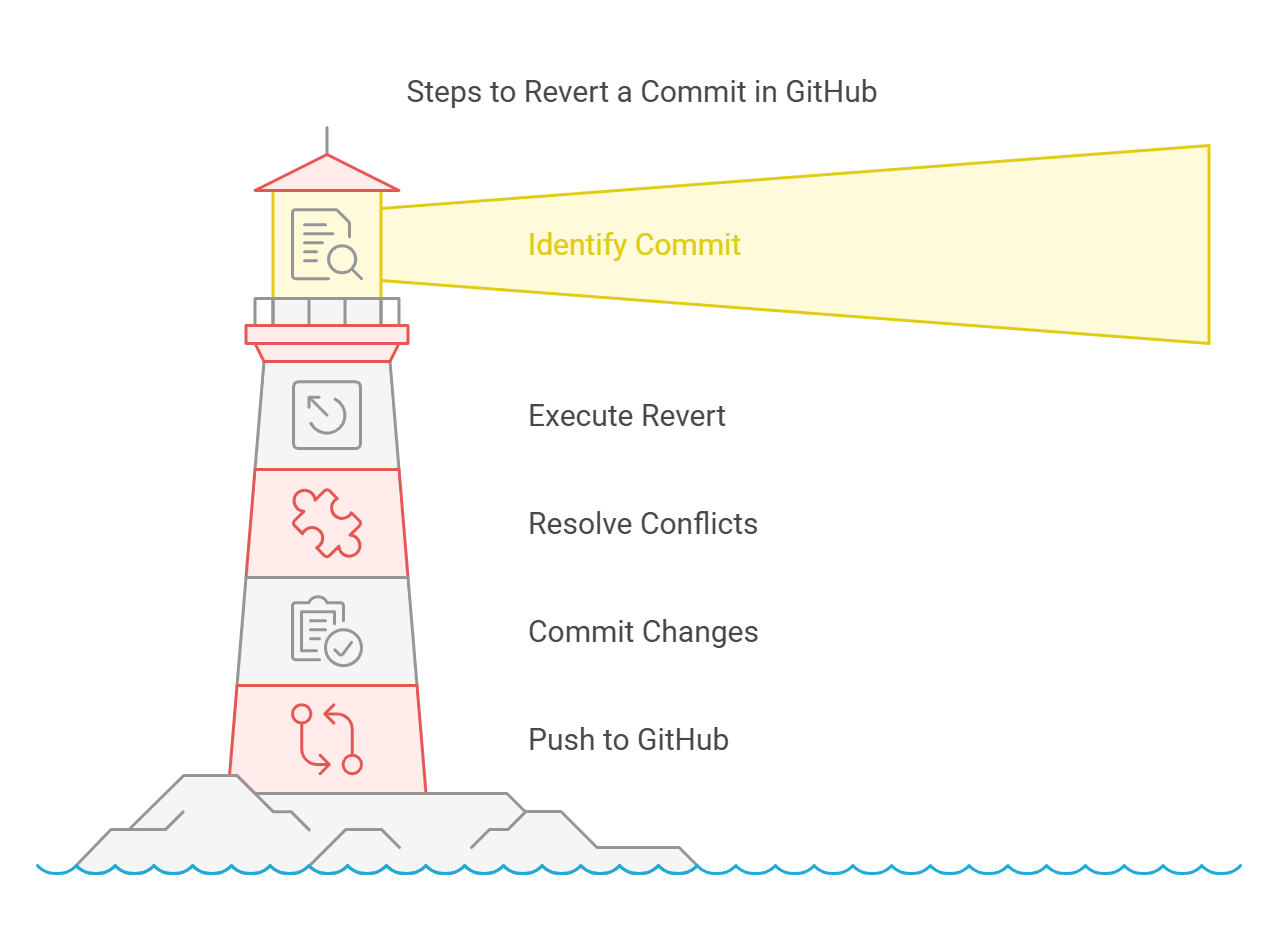
How to Revert to a Previous Commit in GitHub
There are different methods to revert to a previous commit, depending on whether you’re using the GitHub website, the GitHub Desktop app, or the command line. Below, we cover the most common approach—reverting using Git from the command line.
Step 1: Find the Commit to Revert To
Before you can revert, you need to identify the commit you want to go back to. Every commit in Git has a unique SHA-1 hash (a long string of numbers and letters), which is used to identify it.
To view your commit history, open your terminal and navigate to your project’s directory. Then, type the following command:
This command will display a list of commits, showing each commit’s SHA-1 hash, author, date, and commit message. Scroll through the list and find the commit you want to revert to.
Step 2: Revert the Commit
Once you’ve identified the commit you want to revert to, you can use the following command to revert it:
git revert <commit-hash>
<commit-hash> with the actual SHA-1 hash of the commit you want to revert to. For example:git revert a1b2c3d4
This command will create a new commit that undoes the changes made by the commit you specified.
Step 3: Resolve Any Conflicts
Git might encounter conflicts if the changes you’re reverting affect the same parts of the code that have been modified by later commits. In such cases, Git will mark the conflicting files and ask you to resolve the conflicts manually.
To check for conflicts, use:
git status
If there are conflicts, open the files marked by Git, manually edit them to resolve the conflicts, and then stage the resolved files:
git add <conflicted-file>
Step 4: Commit the Revert
After resolving any conflicts, commit the changes with the following command: