The Future of Artificial Intelligence: Opportunities and Challenges
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just a concept for sci-fi movies; it is an evolving force reshaping industries, economies, and society. With advancements in machine learning, natural language processing, and robotics, AI is opening up a world of possibilities that were once unimaginable. However, with its growth come important questions and challenges about its ethical implications, its role in the workforce, and its potential impact on human society.
In this article, we’ll explore the exciting opportunities AI presents, the challenges it brings, and what the future might hold.
1. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence
AI encompasses a range of technologies designed to perform tasks that traditionally require human intelligence. These tasks include recognizing speech, interpreting visual data, making decisions, and learning from experience. Machine learning (ML), deep learning, and neural networks are some of the most prominent AI techniques. With these technologies, AI systems are becoming more capable of performing complex tasks with increasing precision.
In recent years, AI has moved from academic research to real-world applications in a variety of fields, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and customer service. Companies are leveraging AI to automate processes, enhance decision-making, and improve the customer experience.
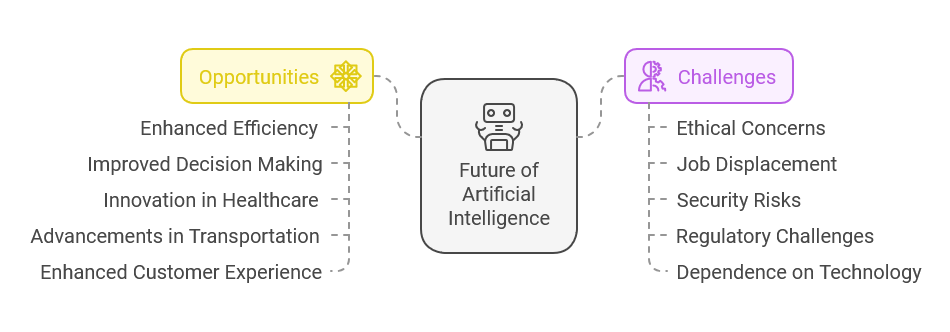
2. Opportunities AI Brings Across Industries
The possibilities of AI are vast, and its impact is already being felt in several key sectors.
Healthcare:
AI is revolutionizing healthcare by improving diagnostics, predicting diseases, and personalizing treatment. AI-powered tools can analyze medical imaging, predict patient outcomes, and help doctors make more informed decisions. For example, AI has been instrumental in detecting early signs of diseases like cancer and Alzheimer’s by analyzing data from medical records, imaging scans, and even genetic information. The potential for AI to reduce human error and improve patient outcomes is vast.
Finance:
In the financial sector, AI is enhancing security, risk management, and fraud detection. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of financial data in real time to identify potential fraud or market trends. Additionally, robo-advisors, powered by AI, are increasingly being used to help investors manage their portfolios with greater efficiency and lower costs.
Transportation:
AI is playing a significant role in transforming transportation with the development of autonomous vehicles. Self-driving cars and trucks, which use AI to navigate roads, make decisions, and avoid accidents, have the potential to reshape the future of mobility, reducing accidents and improving efficiency. AI is also improving traffic management and logistics, optimizing delivery routes, and reducing fuel consumption.
Customer Service:
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are revolutionizing customer service. These systems can handle a variety of customer inquiries, troubleshoot issues, and provide solutions, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction. The adoption of AI in customer service not only enhances user experience but also allows businesses to operate 24/7 without the need for human intervention.
3. The Challenges of AI: Ethical, Economic, and Social Implications
While the opportunities of AI are vast, there are several challenges and concerns associated with its rapid growth.
Job Displacement:
One of the most significant concerns is AI’s impact on the workforce. As AI continues to automate tasks traditionally done by humans, there are fears that large numbers of jobs could be displaced. Roles in manufacturing, retail, and even sectors like finance and healthcare may be at risk as AI becomes more capable of performing tasks faster and more efficiently than humans. However, some argue that AI will create new jobs, particularly in areas like AI development, maintenance, and oversight.
Ethical Issues:
AI raises important ethical concerns. For instance, biases in AI algorithms can result in discrimination in hiring, lending, or law enforcement decisions. If AI systems are trained on biased data, they can reinforce existing inequalities. Moreover, the lack of transparency in AI decision-making processes can make it difficult for individuals to understand how decisions are made or appeal them.
Another ethical dilemma revolves around privacy. AI systems often rely on large datasets, including personal information, to function effectively. This has raised concerns about data privacy, surveillance, and consent, especially as AI is deployed in areas such as facial recognition and online tracking.
AI in Warfare:
The use of AI in military applications, such as autonomous weapons and surveillance systems, poses risks in terms of accountability and decision-making in conflict zones. The ethical implications of AI-driven warfare, where machines may decide the fate of lives without human intervention, are a major topic of debate.
4. The Role of AI in the Workforce: Augmentation or Replacement?
The role of AI in the workforce is one of the most debated topics in the realm of AI. Will AI augment human workers, or will it replace them entirely? The answer likely lies somewhere in between.
AI will most likely automate repetitive, mundane tasks, freeing up human workers to focus on more complex, creative, and strategic responsibilities. For instance, AI can handle data entry, analysis, and routine customer queries, while humans can focus on relationship-building, innovation, and problem-solving. In this way, AI acts as an augmentation rather than a replacement.
However, the workforce needs to adapt to these changes. Retraining and reskilling programs will be necessary to help workers transition to new roles in a technology-driven economy. Governments and organizations will need to invest in workforce development to ensure that employees are equipped with the skills needed for the jobs of the future.
5. The Future of AI: What’s Next?
As AI continues to evolve, its potential is limitless. In the next decade, we can expect several key developments:
- General AI: Current AI systems are designed to excel in specific tasks (narrow AI). However, the development of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)—machines that possess the ability to understand and perform any intellectual task that a human can—could transform industries in ways we cannot fully comprehend yet.
- AI Ethics and Governance: As AI becomes more integrated into our daily lives, the need for robust ethical frameworks and governance structures will become even more pressing. Efforts to create fair, unbiased, and transparent AI will gain momentum, and international agreements will likely be needed to regulate its use.
- AI and Human Collaboration: Instead of replacing humans, AI will increasingly work alongside us, acting as a tool to enhance human capabilities. Future AI systems will assist in complex decision-making, creativity, and problem-solving, while humans remain the final decision-makers.Artificial IntelligenceArtificial IntelligenceArtificial IntelligenceArtificial Intelligence
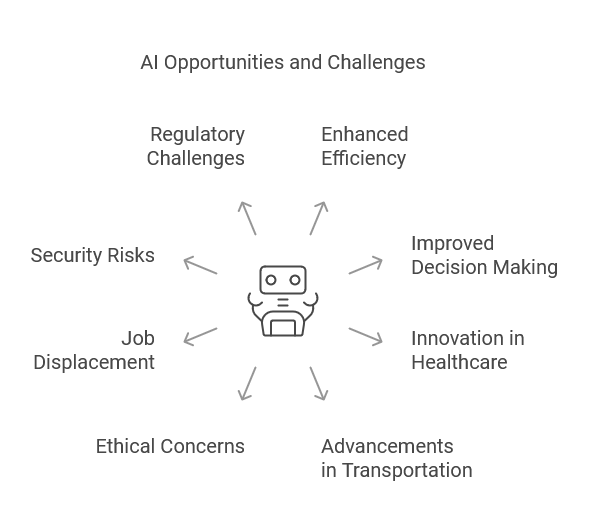
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of AI
Artificial Intelligence presents unprecedented opportunities for innovation and improvement across numerous industries. From healthcare and finance to transportation and customer service, AI has the potential to make our lives easier, more efficient, and more connected. However, as we embrace these advancements, we must also address the challenges AI presents—especially in terms of ethics, privacy, and job displacement.
The future of AI is not something to fear, but something to prepare for. By fostering a collaborative approach between technology, businesses, and governments, we can ensure that AI remains a force for good, driving progress while mitigating its risks. As we move forward, it’s essential to keep in mind that AI’s true potential lies not in replacing humans, but in augmenting our abilities and improving the world we live in.
Artificial IntelligenceArtificial IntelligenceArtificial IntelligenceArtificial Intelligence

